Pamphlet
Antenatal HIV Testing - the Concern of an Expectant Mother
Download PDF file of the bilingual pamphlet for printing
Download PDF file of other languages for printing:Simplified Chinese│Tagalog│Urdu│Indonesian│Nepali│Hindi│Thai│Vietnamese│Sinhala│Bengali

The Aim of Antenatal Check-up
The aim of an antenatal check-up is to ensure optimal health of a pregnant woman throughout her pregnancy. Early detection and appropriate management of health problems help preserve the well-being of both the mother and the foetus. Antenatal check-up generally includes blood testing for blood group, hemoglobin level, mean red cell volume, Rhesus factor, rubella, hepatitis B, syphilis and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
How does Universal Antenatal HIV Testing benefit the pregnant woman?
The transmission routes of HIV include sexual intercourse, blood contact or mother-to-child transmission. After entering the human body, the virus replicates and destroys the lymph cells. It gradually lowers the body’s resistance, leading to opportunistic infections or even cancer and ultimately death.
Among mother-to-child transmission, HIV can transmit from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy, delivery or breastfeeding. Without intervention, the transmission rate from an infected mother to her baby is 15 to 40%. The rate can be reduced to 1-2% with effective treatment and prevention given in the course of pregnancy, during delivery and to the baby after birth.
Treatment and Prevention
- An infected pregnant woman should start antiretroviral therapy (ART) as soon as possible; intravenous ART may also be needed during delivery.
- Discuss the risks and benefits of caesarean section versus vaginal delivery with their doctors.
- Breastfeeding of the newborn should be avoided.
- The baby has to continue oral ART and to be followed up by the paediatrician after birth for the prevention and early detection of complications.
- Once confirmed to be infected, the baby will be given appropriate treatment, and follow-up care to improve his/her health.
The Interpretation of HIV Test Result
A conventional HIV test may take more than one week to process. The test result could be negative (-ve) or positive (+ve). The following is the interpretation of the results:
Negative result (-ve)
- A negative result indicates that the pregnant woman is not infected by HIV at the time of HIV testing. However, one has to be aware of the ‘window period’. Window period is the period between the moment a person gets infected with HIV and when the HIV test shows a positive result. The window period for HIV testing is 3 months. A negative result still cannot exclude infection if the user has recent exposure in the previous 3 months. Users must take note of this and repeat the test or consult a doctor whenever in doubt.
- A pregnant woman who has a negative HIV blood result should continue with preventive measures to protect herself and the foetus against transmission of HIV during the course of pregnancy and breastfeeding. This includes practising safer sex such as condom use, refraining from needle sharing and avoidance of any high risk behaviours.
- Any pregnant woman who in doubt of her HIV status during the course of pregnancy should contact her doctor to perform the HIV test again.
Positive result (+ve)
- A positive result means that the pregnant woman has got infected with HIV. There is a risk of transmitting the virus to the foetus and to her sexual partner through sexual intercourse.
HIV test result is strictly confidential.
Early Detection – How does it benefit the pregnant woman?
- The earlier the infection is detected, the better outcome it will be.
- Apart from quality antenatal care, health care providers work together to develop the best management plan to achieve holistic care in the infected person.
- The pregnant woman will be offered ART as soon as possible to control the HIV disease.
- Through counselling, the pregnant woman will understand her physical and psychological capacity to cope with the disease, and reach consensus about continuation with pregnancy.
- The pregnant woman may choose to disclose her HIV status to her sexual partner or family. The health care provider will offer her and her family support and counselling.
- The infected mother will continue drug treatment and follow-up of the disease after delivery to maintain her health and to prevent complications. She will learn how to take care of her baby and beware of the blood borne transmission.
The Aim of Rapid HIV test
It is important that a pregnant woman knows her HIV status before delivery. In Hong Kong, all pregnant women are routinely tested for HIV in the antenatal check-up. Therefore, for any woman who is about to deliver and who does not know her HIV status yet, a rapid HIV test that takes only minutes SHOULD be done immediately so that appropriate steps can be taken to protect the baby. Result of the test can be read after 20 minutes.
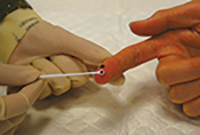
What is rapid test and how is it performed?
- This test shows whether a person is infected with HIV.
- The blood specimen is obtained by fingerprick. A small droplet of blood is taken from your finger and the test result can be read after 20 minutes.
- The rapid HIV test result could be negative (-ve) or positive (+ve). Any positive rapid test result should be followed by confirmatory test of venous blood conducted by a laboratory.


For the protection of both yourself and the baby, please consider antenatal HIV testing. Early diagnosis benefits both you and your baby.
Should you have further queries about HIV test and HIV infection, please talk to your doctor or nurse. You are also welcomed to contact our counsellor via the AIDS Hotline at 2780 2211.